Resolving blockage
Lymphatic drainage / Edema therapy
What is lymphatic drainage?
In lymphatic drainage, we use manual techniques to drain any fluid and accumulated lymph into the tissue and lymph vessels. In contrast to the blood vessels through which the blood is driven from the heart, lymph collects in the lymph vessels throughout the whole body, and is discharged only through muscular activity, especially the large muscle groups, and external influences. In lymphatic drainage, the hands of the therapist function like a pump: they activate the lymphatic system and help to loosen the accumulating lymph, which can create swelling or thicken extremities. Other tissue fluids can also be mobilized and transported through gaps between or the lymphatic system.
How does lymphatic drainage work?
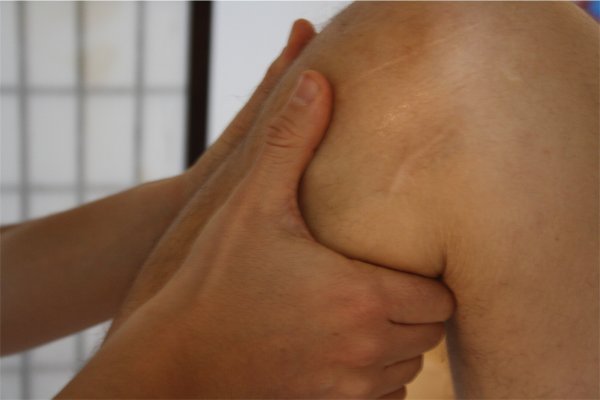
From the outside, lymphatic drainage looks just like a normal massage. However, in it we use a certain technique with rhythmic, orbital pumping movements. The therapist’s hands lie flat on the body of the patient, and “push” any fluid accumulations (edema) that can be felt in the tissue. Using carefully measured degrees of pressure, region by region is treated according to the clinical picture. The treatment goes deeper only in the case of special types of drainage, for example, in the case of special techniques on the adductor gap, or also when we use balloon drainage, where the patient's breathing rhythm helps us to reach deeper lymphatic systems.
In order to support the lymphatic drainage and to prevent or slow the return of water (edema) in the treated limbs, we tend to bind them after the treatment or use a suitable compress (on the legs, for example, a compression stocking). We can treat the following types of edema with this therapy:
- Lymphatic edema
- Phlebedema
- Traumatic edema
- Sudeck disease
- Artificial and ischemic edema
- Rheumatic edema
- Chronic inflammatory edema (scleroderma, radiation damage)
- Edema due to inactivity (in case of paralysis)
- Lipedema
- Idiopathic edema
In addition, manual lymph drainage is an important building block during recovery after surgical procedures in which lymph nodes have been removed.