Gentle massage technique to promote lymph flow, reduce swelling and support healing.
- muscle tension and pain
- chronic muscle or tendon pain
- support for the healing process of broken bones
- improvement of tissue elasticity
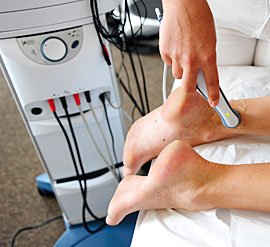
Ultrasound therapy is a well-established method in physical therapy. Using sound waves in the frequency range between 20 kHz and 800 kHz, it stimulates the body's self-healing processes and relieves pain.
Treatment Procedure
Continuous or pulsed ultrasound is used depending on the patient's needs. The sound waves act directly on the affected tissue or stimulate afferent nerves. One area is treated for about 1 to 2 minutes. In chronic cases, the therapy may last up to 10 minutes. The ultrasound strength ranges from 0.05 to 1.5 watts per square centimetre and is adjusted individually.
Positive Effects of the Therapy
The sound waves generate vibrations that resemble an intensive connective tissue massage, stimulating blood circulation. The tissue warms up due to the absorption of the sound energy. This can help release muscle tension and support the healing process.
Safe and Targeted Use
In areas near bones, pulsed ultrasound is used exclusively, as it produces significantly less heat. This ensures gentle tissue treatment and prevents potential overheating.